Horsepower Calculator
Horsepower: N/A HP
Understanding Horsepower: A Comprehensive Guide
What is Horsepower?
Horsepower is a unit of measurement that quantifies the power output of engines, particularly in vehicles like cars, trucks, and motorcycles. The term was coined by James Watt, an 18th-century engineer who sought a way to compare the power of steam engines with that of draft horses. Today, horsepower remains a critical metric in the automotive and engineering industries, providing insight into an engine's performance and capability.
Origins of Horsepower
The concept of horsepower was developed by James Watt, who is also known for his work on improving the steam engine. Watt observed that a horse could turn a mill wheel 144 times in an hour, lifting a 550-pound weight one foot in one second. From this observation, he defined one horsepower as the ability to do 550 foot-pounds of work per second. This definition provided a standard measure of engine power, allowing for comparisons between different engines and the work they could perform.
Types of Horsepower
- Mechanical Horsepower: The original definition by Watt, where 1 horsepower equals 550 foot-pounds per second.
- Metric Horsepower: Used in Europe, where 1 metric horsepower equals 735.5 watts, slightly different from the mechanical horsepower.
- Brake Horsepower (BHP): The power output of an engine measured at the crankshaft before any losses from the gearbox, alternator, differential, water pump, and other auxiliary components.
- Shaft Horsepower (SHP): Power delivered to the propeller shaft of a ship or an airplane, taking into account losses from the gearbox.
- Electrical Horsepower: Used to measure the output of electric motors, where 1 horsepower equals 746 watts.
Calculating Horsepower
Horsepower can be calculated using various methods, depending on the type of engine and the available data. For internal combustion engines, the most common formula involves torque and rotational speed (RPM):
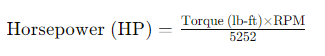
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how this formula works:
- Torque (lb-ft): Torque is a measure of the rotational force the engine produces. It is usually measured in pound-feet (lb-ft).
- RPM (Revolutions Per Minute): RPM indicates how fast the engine is spinning. It’s a measure of the number of full rotations the engine’s crankshaft makes in one minute.
- Constant (5252): The constant 5252 is derived from the relationship between horsepower, torque, and RPM, based on the definitions of these units.
Example Calculation
Consider an engine that produces 300 lb-ft of torque at 4000 RPM. To calculate the horsepower:

Thus, the engine produces approximately 228.48 horsepower at 4000 RPM.
Factors Affecting Horsepower
Several factors can influence the horsepower output of an engine:
- Engine Size and Design: Larger engines with more cylinders typically produce more horsepower.
- Fuel Type: High-octane fuel can improve performance and increase horsepower.
- Air Intake and Exhaust Systems: Improved airflow into and out of the engine can enhance combustion efficiency and power output.
- Turbocharging and Supercharging: Forced induction systems compress more air into the engine, allowing for more fuel to be burned and thus more power produced.
- Engine Tuning: Adjusting the engine’s timing, fuel injection, and other parameters can optimize performance and increase horsepower.
Practical Applications of Horsepower
Horsepower is not just a theoretical measure; it has practical implications in various fields:
- Automotive Industry: Horsepower is a key factor in determining the performance of cars and trucks, influencing acceleration, towing capacity, and top speed.
- Marine Engines: In boats and ships, horsepower affects cruising speed and the ability to navigate through challenging conditions.
- Aviation: Aircraft engines are rated in horsepower to ensure they can provide the necessary thrust for takeoff, cruising, and landing.
- Industrial Machinery: Many industrial machines, such as generators and pumps, are rated in horsepower to indicate their power output and efficiency.
Conclusion
Horsepower is a crucial metric in understanding the power and performance of engines across various applications. By calculating horsepower using torque and RPM, engineers and enthusiasts can gauge an engine's capability and compare it with others. Whether you’re buying a car, a boat, or an industrial machine, knowing its horsepower helps you make an informed decision about its performance and suitability for your needs.
Understanding horsepower and its calculation not only enhances your knowledge of engineering principles but also empowers you to appreciate the marvels of modern machinery and their impressive capabilities.
![]()

